Creating ECS Capacity for Elastic Container Service (ECS)
Overview
Amazon ECS capacity is the infrastructure where your containers run.
The following is an overview of the capacity options:
- Amazon EC2 instances in the AWS cloud: You choose the instance type, the number of instances, and manage the capacity.
- Serverless (AWS Fargate) in the AWS cloud: Fargate is a serverless, pay-as-you-go compute engine. With Fargate, you don’t need to manage servers, handle capacity planning, or isolate container workloads for security.
- On-premises virtual machines (VM) or servers: Amazon ECS Anywhere provides support for registering an external instance such as an on-premises server or virtual machine (VM), to your Amazon ECS cluster.
ECS cluster capacity providers and ECS capacity are not the same.
ECS capacity is referring to the infrastructure capacity that is available to run tasks and services within an ECS cluster. This capacity can be provisioned using capacity providers.
The capacity provider strategy then determines how tasks get distributed to the different infrastructure sources within the cluster. This helps optimize resource usage and cost based on the task requirements. Each cluster has one or more capacity providers and an optional default capacity provider strategy. The capacity provider strategy determines how the tasks are spread across the capacity providers. When you run a task or create a service, you may either use the cluster’s default capacity provider strategy or specify a capacity provider strategy that overrides the cluster’s default strategy.
Steps
Retrieve ECS-optimized AMI
# Get ECS AMI ID ecs_instance_ami_id=$(aws ssm get-parameters \ --names /aws/service/ecs/optimized-ami/amazon-linux-2/recommended \ --region $region | jq -r '.Parameters[0].Value | fromjson.image_id')Here we use Amazon Linux 2 as the base operating system; for other base operating systems, refer to Retrieving Amazon ECS-Optimized AMI metadata
Create Launch Template with Amazon ECS-optimized AMI
The ECS agent is a containerization tool used by ECS to manage instances. To let the ECS agent know which cluster this instance belongs to, you need to configure the following in the /etc/ecs/ecs.config file:
ECS_CLUSTER=ecs_cluster_nameecs_instance_type=t3.medium ecs_instance_subnet_id=$subnet_public_1 ecs_launch_template_name=$project-ecs-launch-template # Create Launch template file cat <<EOF | tee ecs-launch-template.json { "ImageId": "$ecs_instance_ami_id", "InstanceType": "$ecs_instance_type", "IamInstanceProfile": { "Arn": "$ecs_instance_profile_arn" }, "NetworkInterfaces": [{ "DeviceIndex": 0, "AssociatePublicIpAddress": true, "Groups": ["$ecs_instance_sgr_id"], "SubnetId": "$ecs_instance_subnet_id" }], "KeyName": "$ecs_instance_key_name", "TagSpecifications": [{ "ResourceType": "instance", "Tags": `echo '['$tagspec | sed 's/{/{"/g; s/}/"}/g; s/,/","/g; s/}","{/},{/g; s/=/":"/g'` }], "UserData": "`cat <<EOF | openssl base64 -A #!/bin/bash echo ECS_CLUSTER=$ecs_cluster_name >> /etc/ecs/ecs.config EOF`" } EOF # Create launch template using the created launch template file aws ec2 create-launch-template \ --launch-template-name $ecs_launch_template_name \ --launch-template-data file://ecs-launch-template.jsonCreate Auto Scaling Group using the template created
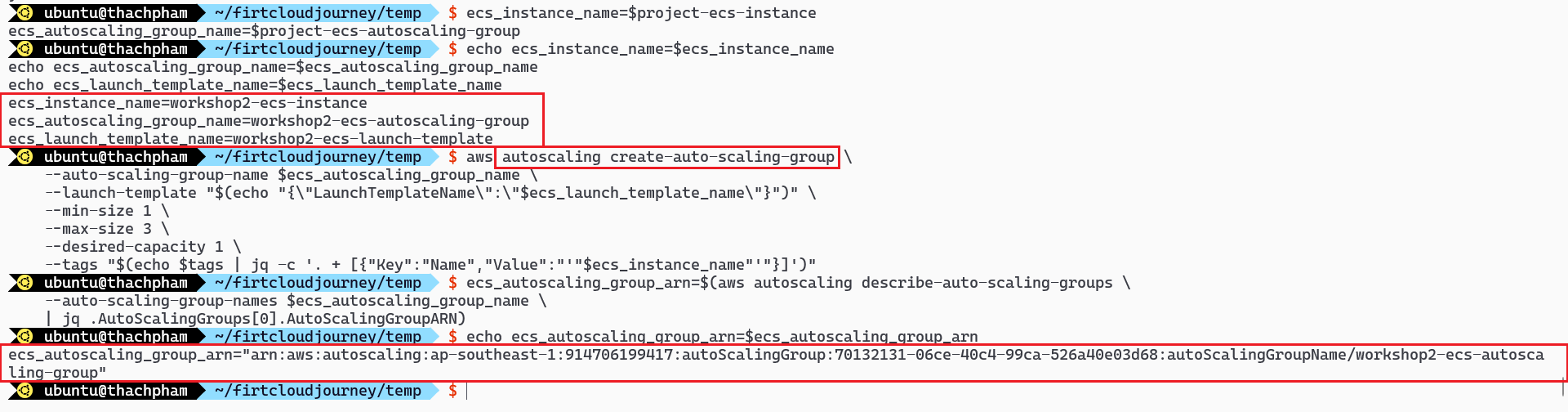
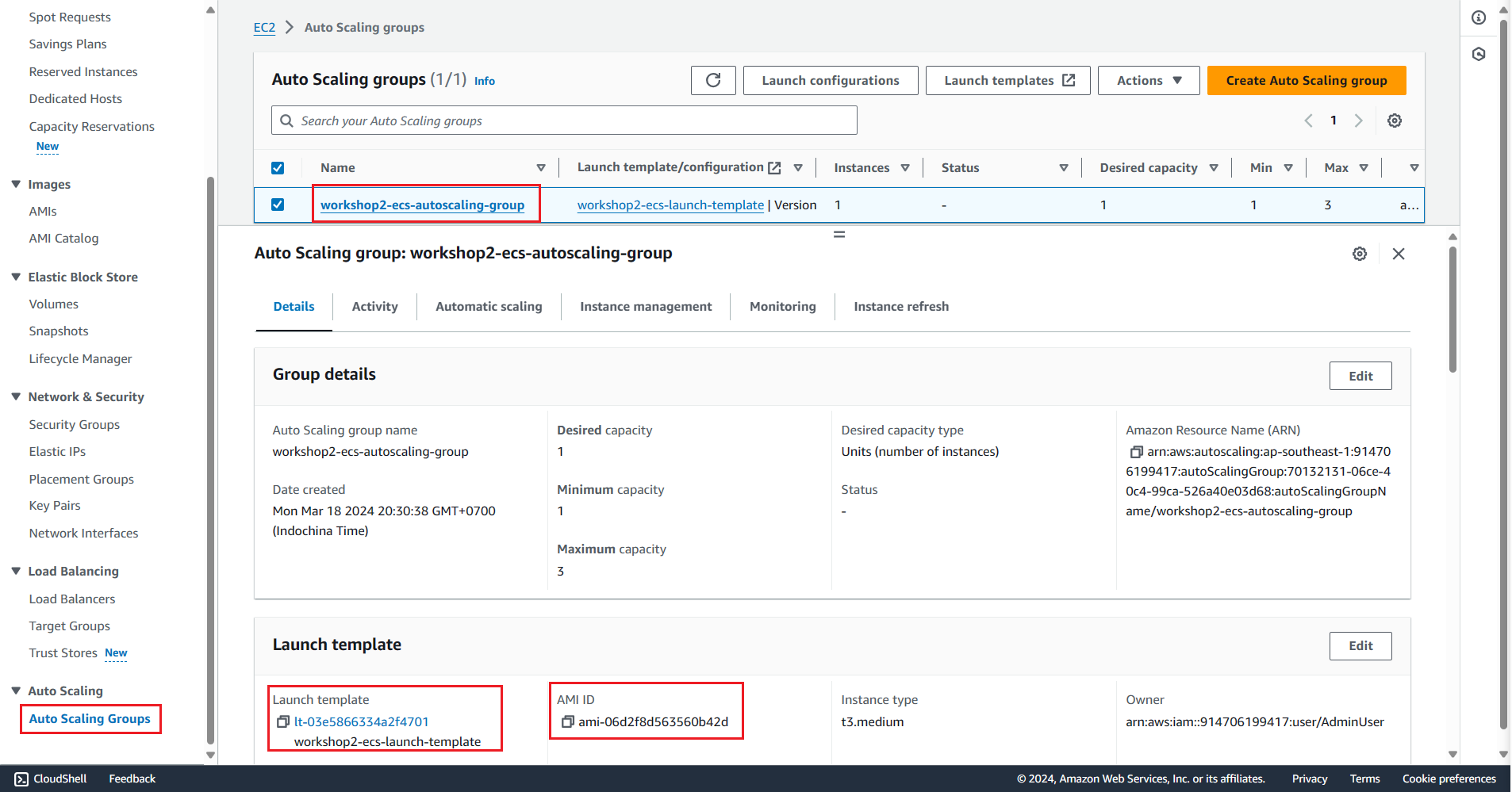
ecs_instance_name=$project-ecs-instance ecs_autoscaling_group_name=$project-ecs-autoscaling-group # Create Autoscaling group aws autoscaling create-auto-scaling-group \ --auto-scaling-group-name $ecs_autoscaling_group_name \ --launch-template "$(echo "{\"LaunchTemplateName\":\"$ecs_launch_template_name\"}")" \ --min-size 1 \ --max-size 3 \ --desired-capacity 1 \ --tags "$(echo $tags | jq -c '. + [{"Key":"Name","Value":"'"$ecs_instance_name"'"}]')" ecs_autoscaling_group_arn=$(aws autoscaling describe-auto-scaling-groups \ --auto-scaling-group-names $ecs_autoscaling_group_name \ | jq .AutoScalingGroups[0].AutoScalingGroupARN)List Container Instance
Check instances in the autoscaling group if they are managed by ECS or not
aws ecs list-container-instances --cluster $ecs_cluster_nameCreate Capacity Provider and use it for ECS Cluster
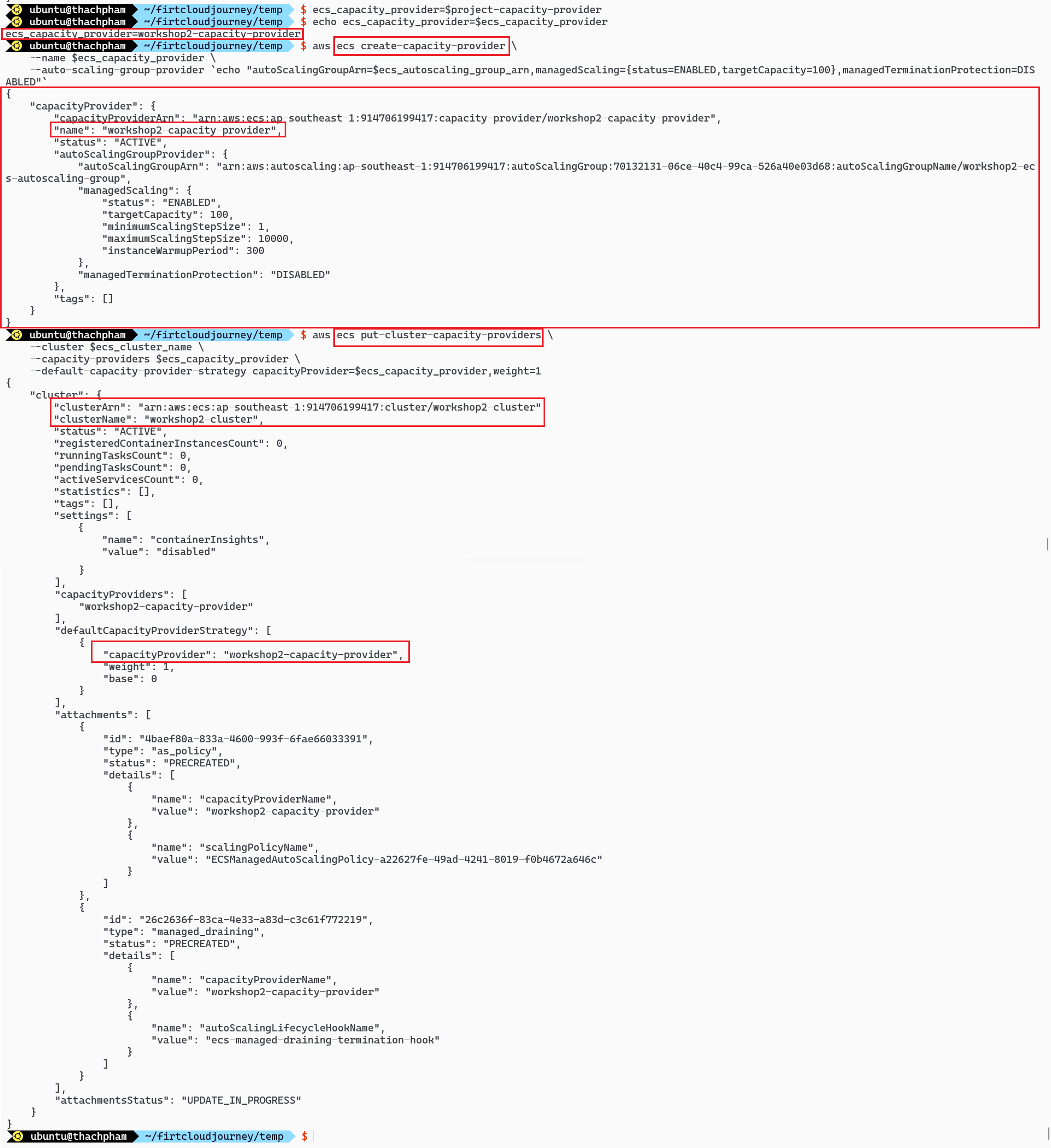
Actually, creating an ECS Capacity Provider in this lab doesn’t make much sense. Mostly for educational purposes to know and understand how to create an ECS Capacity Provider. (This part can be skipped, and the lab will still function 🥲)
ecs_capacity_provider=$project-capacity-provider # Create Capacity provider aws ecs create-capacity-provider \ --name $ecs_capacity_provider \ --auto-scaling-group-provider `echo "autoScalingGroupArn=$ecs_ec2_autoscaling_arn,managedScaling={status=ENABLED,targetCapacity=100},managedTerminationProtection=DISABLED"` \ --tags $tags2 aws ecs put-cluster-capacity-providers \ --cluster $ecs_cluster_name \ --capacity-providers $ecs_capacity_provider \ --default-capacity-provider-strategy capacityProvider=$ecs_capacity_provider,weight=1
Execution
Retrieve ECS-optimized AMI

Create Launch Template
Create content for the Launch Template configuration file
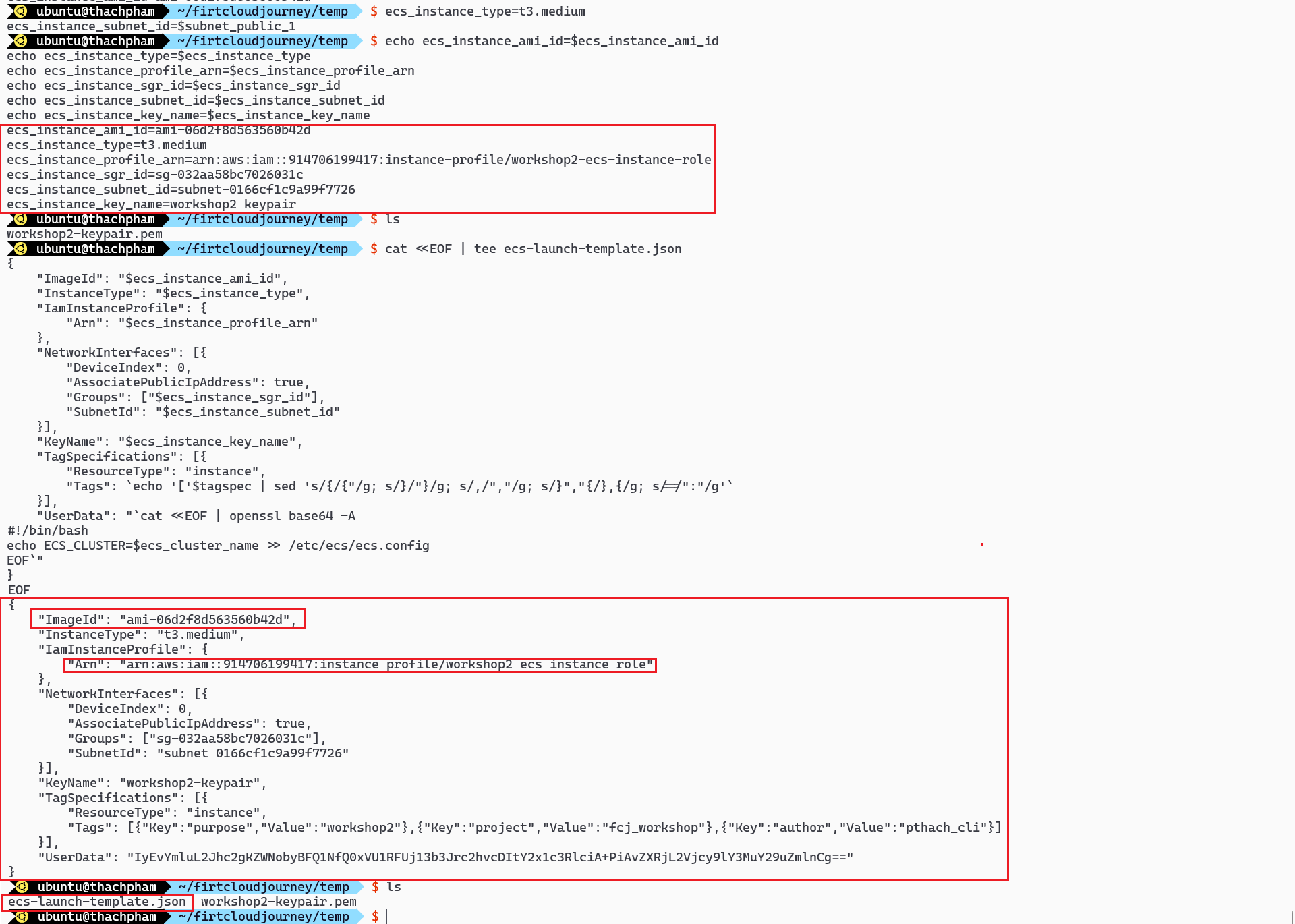
Content of the configuration file and use it to create the Launch Template
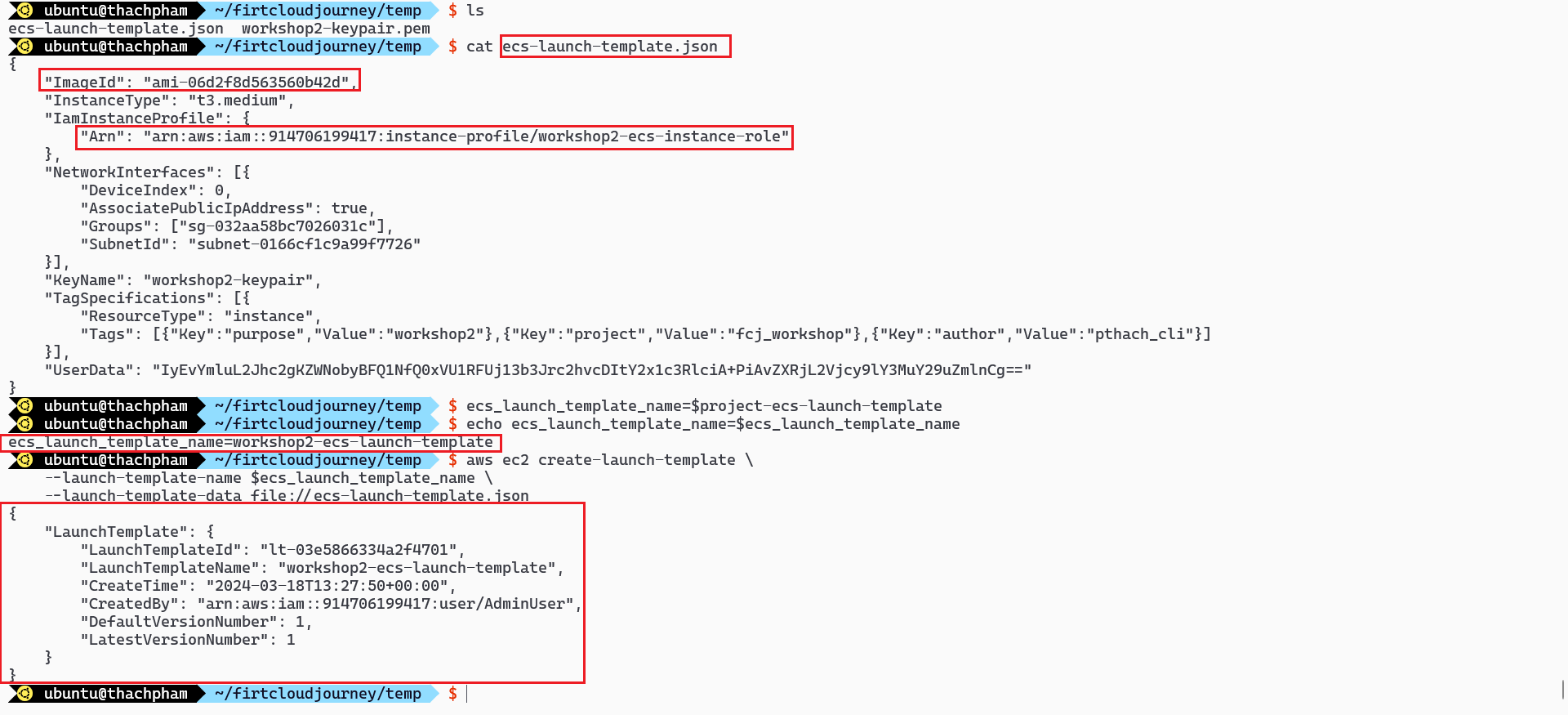
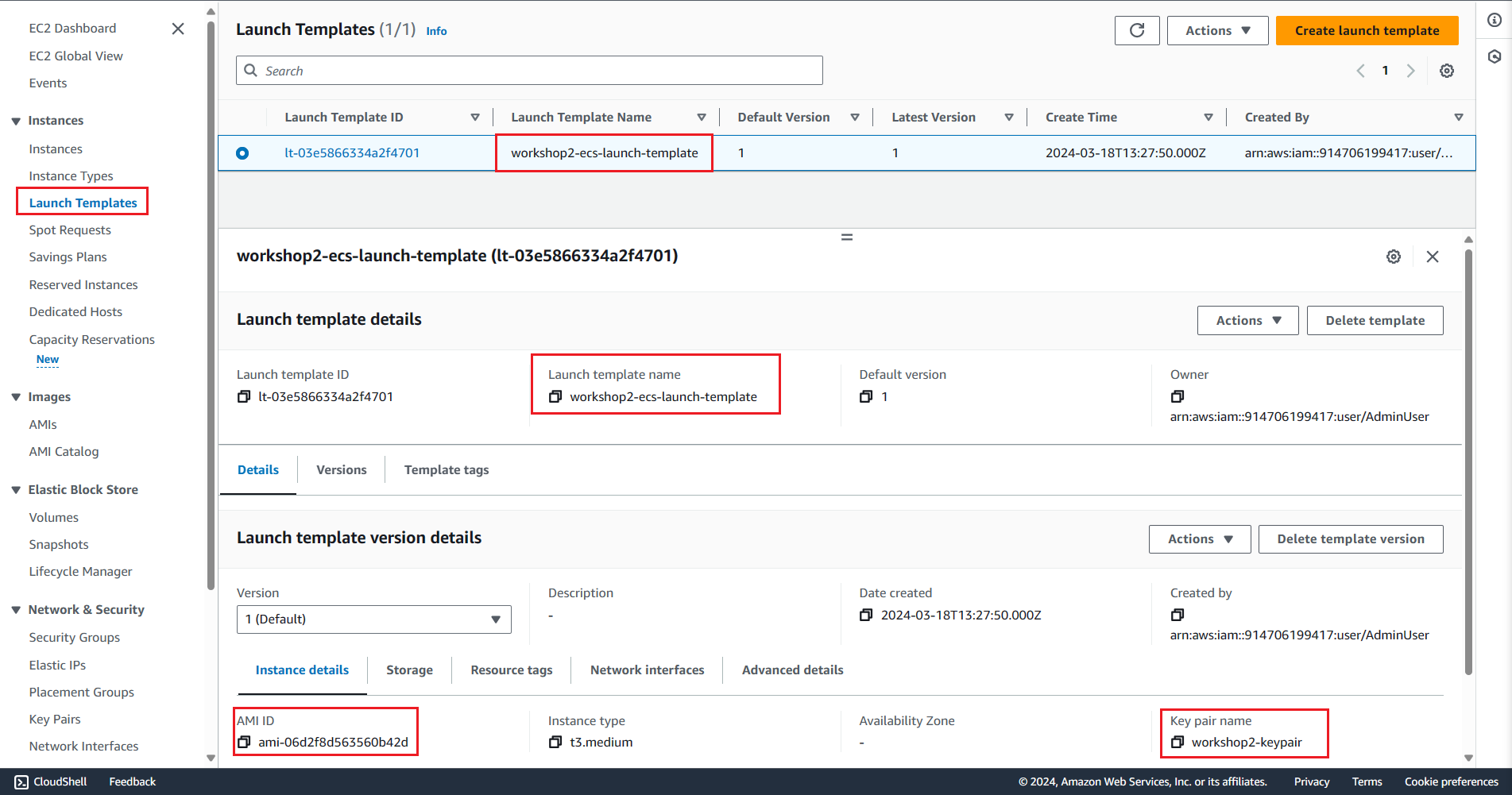
Successful creation of the Launch Template:
Create Auto Scaling Group using the created template
Check the result on the AWS Console
List Container Instances

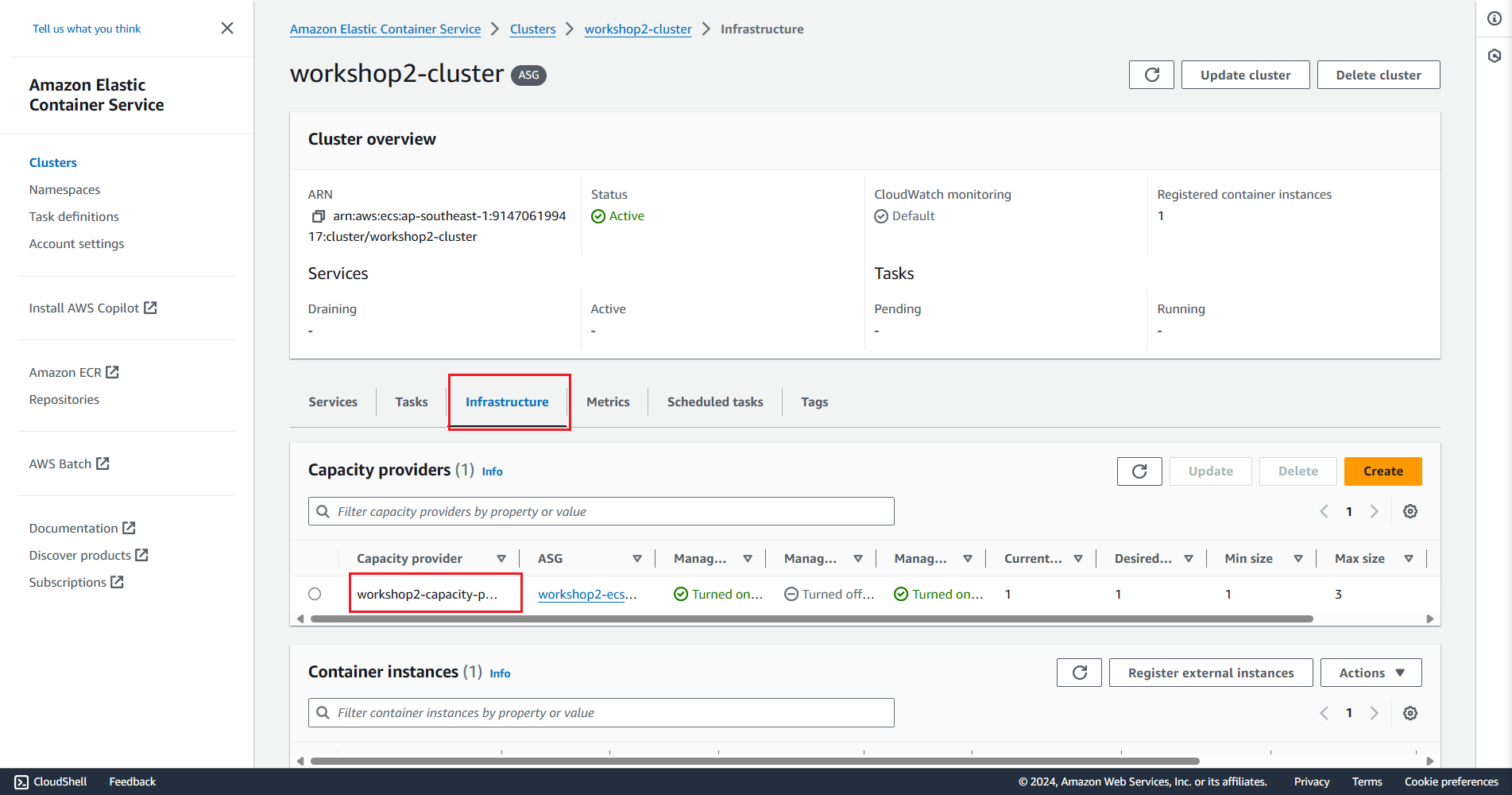
Create Capacity Provider and use it for ECS Cluster
Check the result on the AWS Console
References
| 👉 Why use Capacity Provider if you already have an Auto Scaling Group?
Your auto scaling group scaling works on a service level only. An ECS cluster can have many services running. Therefore, capacity provider runs at cluster level and can scale your container instances based on all the services in the cluster, not only one service.
A highly reliable answer on AWS from StackOverFlow Whats the difference on using a ECS capacity provider and using automatic scaling from auto scaling group in a ECS cluster?
AWS documentation on this topic Creating a cluster with an EC2 task using the AWS CLI
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/instance_IAM_role.html